triton-01-softmax
介绍
Triton是OpenAI开发的一种编程语言,帮助没有CUDA经验的开发者快速编写高性能GPU算子,实现加速。
作为上手的第一次尝试,本文以Softmax为例,体验一下triton的编写流程。Softmax是深度学习中一个基础算子,可用来将原始分数(Logits)转化为概率分布,常用于分类网络。
一维场景:$X,Y \in \mathbb{R}^{N}$
二维场景:$X,Y \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times N}$
这里,$x_i$是一个长度为$N$的向量。
本文使用triton来实现一个二维softmax算子,并与torch softmax对比精度,确认实现的正确性。
Softmax实现
说明:
实验环境:AutoDL 容器 RTX 2080 Ti(11GB)
PyTorch 2.5.1
Python 3.12(ubuntu22.04)
CUDA 12.4
安装triton:
pip install triton |
triton softmax实现(参考openai triton官网实现):
代码:
import triton |
输出结果:
Y_triton = tensor([[7.4673e-04, 5.3404e-03, 5.1782e-04, ..., 3.1986e-03, 2.1141e-04, |
验证了triton和torch softmax输出结果一致。
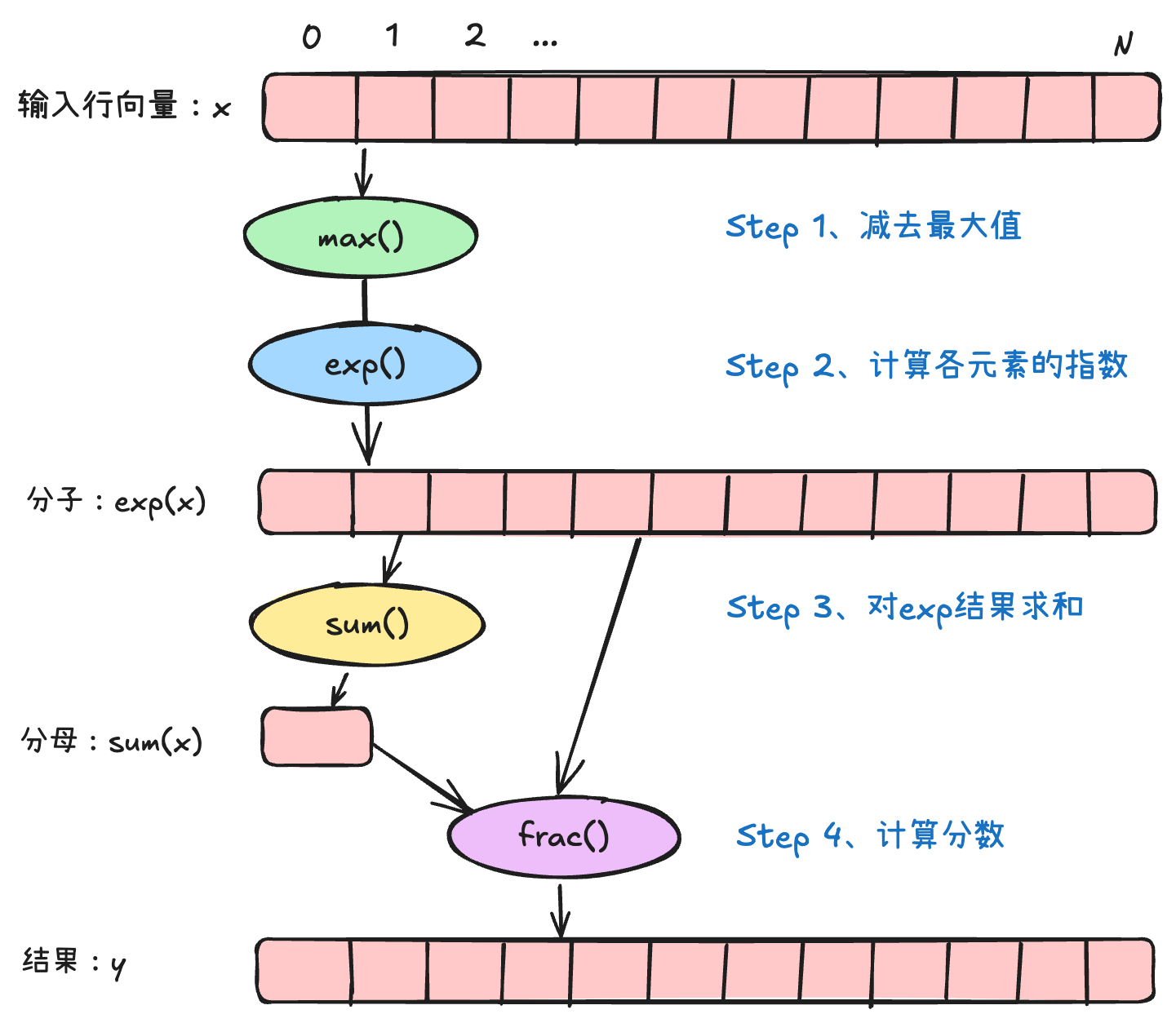
补充:softmax数值计算技巧
当输入x值的范围很大时,exp(x)的数值也很大,会上溢为nan;当所有的x值都接近-inf时,sum(exp(x))就接近0,作为分母容易导致除法不稳定。
这里可以通过数学上的变换小技巧,通过减去x的最大值,可使exp()的值小于1,另外由于$x{max} - x{max} = 0$,由于0的存在,exp(0)=1,不会使得所有分母都接近0,推导如下:
参考
Introducing Triton: Open-source GPU programming for neural networks